ANALYTICAL MOVEMENTS
Just as in general accounting, analytic entries should be related to an account and an analytic journal.
Analytic records can be distinguished from general records by the following characteristics:
- they are not necessarily legal accounting documents
- they do not necessarily belong to an existing accounting period
- they are managed according to their date and not an accounting period
- they do not generate both a debit and a credit entry, but a positive amount (income) or a negative amount (cost).
Even though most analytic entries are produced automatically by the @/Arpro program, it is sometimes necessary to record manual entries. It is usually needed for certain analytic operations which have no counterpart in the general accounts.
Analytic accounting is totally integrated with the general ledger, so you never have to re-enter the records. They are automatically generated by the following operations:
- confirmation of an invoice generates analytic entries for sales or purchases connected to the account shown in the invoice line
- the entry of a service generates an analytic entry for the cost of this service to the given project
- the manufacturing of a product generates an entry for the manufacturing cost of each operation in the product range
Other documents linked to one of these three operations produce analytic records indirectly. For example, when you are entering a customer sales order, you can link it to the customer’s analytic account. When you are managing by case or project, mark the project with that order. This order will then generate a customer invoice, which will be linked to the analytic account. When the invoice is confirmed, it will automatically create general and analytic accounting records for the corresponding project.
Expense receipts from an employee can be linked to an analytic account for reimbursement. When a receipt is approved by the company, a purchase invoice is created. This invoice represents a debit on the company in favor of the employee. Each line of the purchase invoice is then linked to an analytic account which automatically allocates the costs for that receipt to the corresponding project.
Using the analytic model concept, you can distribute your income or expenses to one or several analytic accounts at the same time. Thanks to this model, you can have one amount distributed amongst several analytic accounts that involve different cost/revenue centers.
Just as in general accounting, analytic entries are organized year by year, corresponding to individual accounting records or to manually created movements.
Toolbar
allows to create a manual analytical movement.
deletes the current selected movement.
opens a window where you can define a range (from number to number) of analytical movements to be deleted at the same time.
opens a window that displays all the data related to the accounting record that generated the current movement.
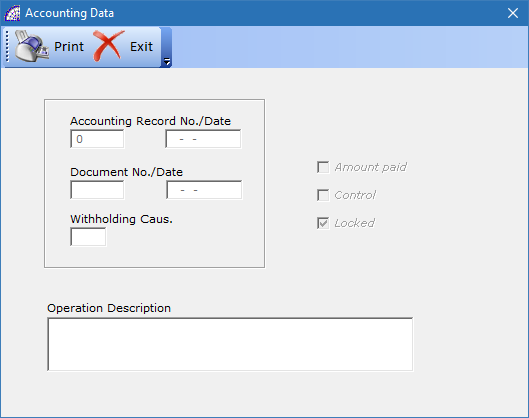
We find the number and date of the accounting entry (Accounting Record No./Date), any reference to the sales or purchase document (Document No./Date), any causal of withholding tax (Withholding Caus.), a standardized description describing the current movement and the related accounting references (Operation Description).
By opening this window from the “Card” tab, some of these fields can be modified as to the values, any other adjustments or to insert more details.
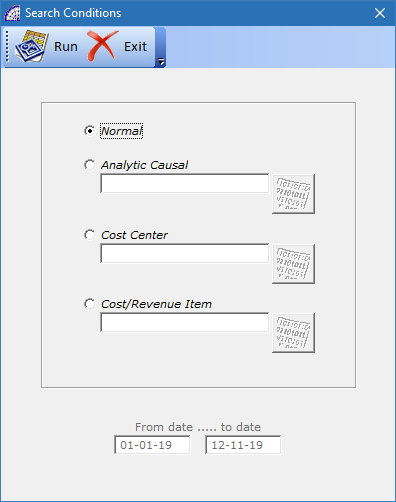
opens a window that displays the available search conditions.
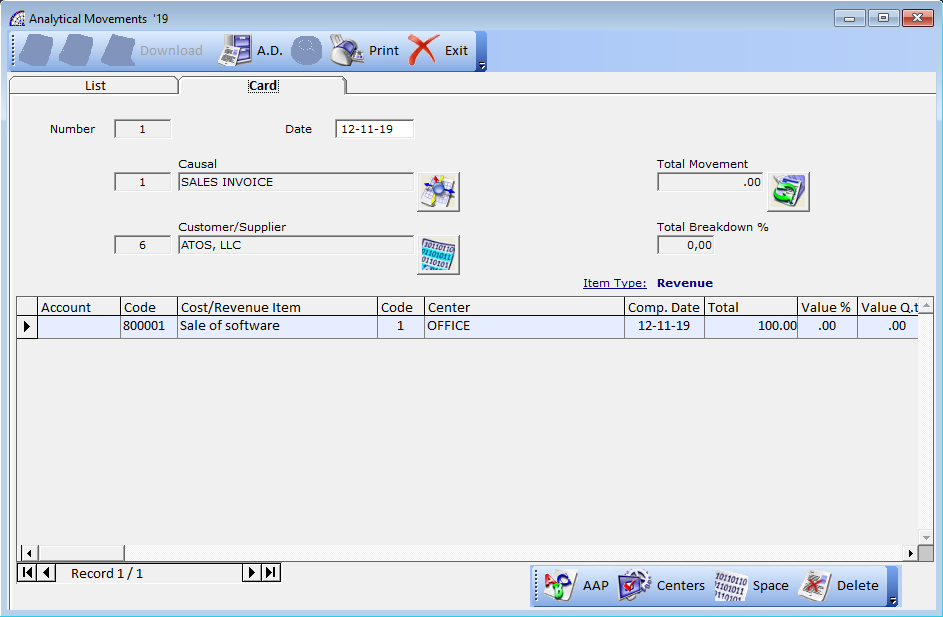
Card Tab
Number: identification number of the movement, automatically managed by the program.
Date: date of the analytical movement.
Causal: defines the analytical causal, which determines whether it is a movement of “Income” or “Expenses”. It is a mandatory field.
Customer/Supplier: defines the reference customer or supplier, in case the movement was generated following the creation of invoices.
Total Movement: displays the total movement defined by the sum of the individual values present in the “Total” column.
Total Breakdown %: displays the total defined by the sum of the individual values present in the “Value %” column.
The amount on the “Total Breakdown %” field has to equal 100, so the values must then be allocated for each account entered in the underlying grid.
Grid Fields
Account: defines the account of the accounting account plan.
Code: defines the code of the analytical accounts plan.
Cost/Revenue Item: description of the analytical account.
Code: displays the center cost/revenue code.
Comp. Date: displays the competence date.
Total: amount of the revenue or cost.
Value %: displays the percentage of allocation of the analytical account.
Value Q.ty: displays the quantity value.
Note: (maximum 10 characters) free note field.
Bottom Toolbar
AAP: allows to choose an account of the analytical accounts plan from the list.
allows to choose a center cost/revenue from the list.
adds a line of space above the cursor position in the grid.
deletes the selected record.
All the command buttons in the toolbar are used to insert or modify data in the case of analytical movements created manually.
JOB ORDERS
Used in the context of production and is part of the analytical management. Please refer to the relative manual for more details.
AUTOMATIC-MOVEMENTS, BUDGET …
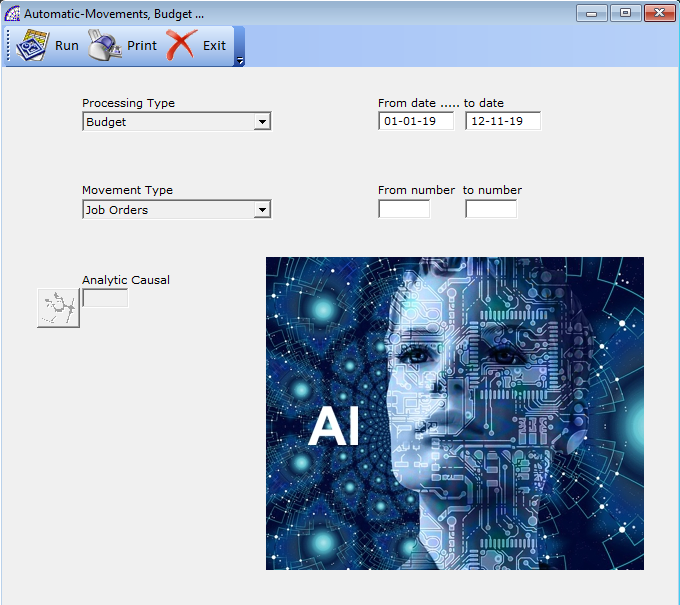
It allows to import data into the analytical movements database, such as real movements from accounting or simply as forward-looking movements (budgets) from job orders, warehouse movements, customer or supplier orders.
A useful tool in the case of having to regenerate analytical movements following a cancellation or simply to update forecast data.
Processing Type: defines the type of data import, for processing “Analytical Movements” or “Budget”.
Movement Type: active only in the case of budget, defines the type of data entry to be imported.
Analytical Causal: defines the type of analytical causal that will be associated with the imported movements. This feature has been frozen for this version of the program.
From date … to date, From number … to number: representing conditions that define the search filter for the data to be imported into the program.
Once these conditions have been defined, pressing the button on the toolbar activates the executing process. In case of budget import, following a request from the program all existing precedents will be deleted.
