QUALITY
A quality management system (QMS) is a set of policies, processes and procedures required for planning and execution (production/development/service) in the core business area of an organization. (i.e. areas that can impact the organization’s ability to meet customer requirements.) ISO 9001 is an example of a Quality Management System.
A QMS integrates the various internal processes within the organization and intends to provide a process approach for project execution. A process based QMS enables the organizations to identify, measure, control and improve the various core business processes that will ultimately lead to improved business performance.
The concept of Quality Management is quite simple, it seeks to:
- recognize interested party requirements including Licenses to Trade, guidelines, customer requirements, and the chosen management system standard(s)
- ensure that all requirements have been met
- confirm that employees receive applicable training in the quality system requirements
- determine processes, their interaction, inputs and outputs
- produce records or evidence that system requirements have been met
- measure, monitor and report the performance of the QMS
- plan changes to the QMS and take actions to address risks and opportunities as a result of changes
- perform internal audit to analyze the QMS and correct nonconformities
- continually improve the QMS
Easier to say than to do it!
@/Arpro Erp, Quality Module can contribute to reach this goal.
A solution perfectly integrated with the production system and the business management program, from which it draws data from the master data, provides some support functions:
- Non-Conformity and Claims
- Non-Conformity Analysis
- Reports of Control
- Audits, Customer Satisfaction, Suppliers, Quality Manual as document managers
- Instruments and equipments
- Corporate Functions
- Non-Conformity Type and Causes
The first steps to follow are to define all the master data in terms of quality, that is to say the corporate functions, non-conformity types and causes.
At the same time and if necessary, it occurs to catalog and describe the various instruments and equipments available in the various departments, also organizing the plans for maintenance and calibrations (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Instruments and Equipments” + …).
Start scheduling staff training activities after auditing by including these documents in the planned section of the program (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Audits”).
The central element of the whole organization is the “Quality Manual”, a document that states the company’s intentions for operating the processes within the quality management system. It can include policies for all areas of the business that affect your ability to make high quality products and meet your customers’ and ISO’s requirements.
It is therefore necessary to define all the contexts and procedures, saving these documents in the dedicated section of the program (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Quality Manual”).
As far as the data acquisition phases are concerned, the organization of the various documents relating to “Customer Satisfaction” must be defined, a specific document area in the program (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Customer Satisfaction”).
All these quality management documents must therefore be organized, as well as created, perhaps inspired by some existing templates on the web but also considering your specific needs. We can provide different templates to the different areas of expertise, however, we recommend contacting qualified personnel in the consulting area.
Then it is necessary to start collecting a data archive with the non-conformities found, the subsequent solutions adopted, all the data related. In some ways it is statistical, easily analyzed through a graphical tool, to highlight where the anomalies happen more frequently.
The causes of nonconformities aren’t unlimited and therefore determinable. Common causes for deficiencies to arise include:
- poor communication (or miscommunication)
- poor documentation (or lack of documentation)
- poor or limited training of personnel
- poor motivation of personnel
- poor quality materials (or lack of appropriate materials)
- poor quality tools and equipment (or lack of appropriate tools and equipment)
- poor or dysfunctional operating environment
The non-conformities and the corresponding analyzes and corrective treatments are managed in a specific section of the program (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Non-Conformity and Claims”).
The control reports are an integral part of the quality control, divided by year, and memorize the data of the checks carried out in the specific contexts in special sheets (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Control Reports”).
NON-CONFORMITY AND CLAIMS
Handling complaints, non-conformities and any consequent corrective measures to be taken are at the base of every management system, not only for Quality (conforming with ISO 9001, ISO 13845 o ISO-TS 16949), but also for Environment (conforming with ISO 14001) and Safety in the Workplace (there are specific laws about this).
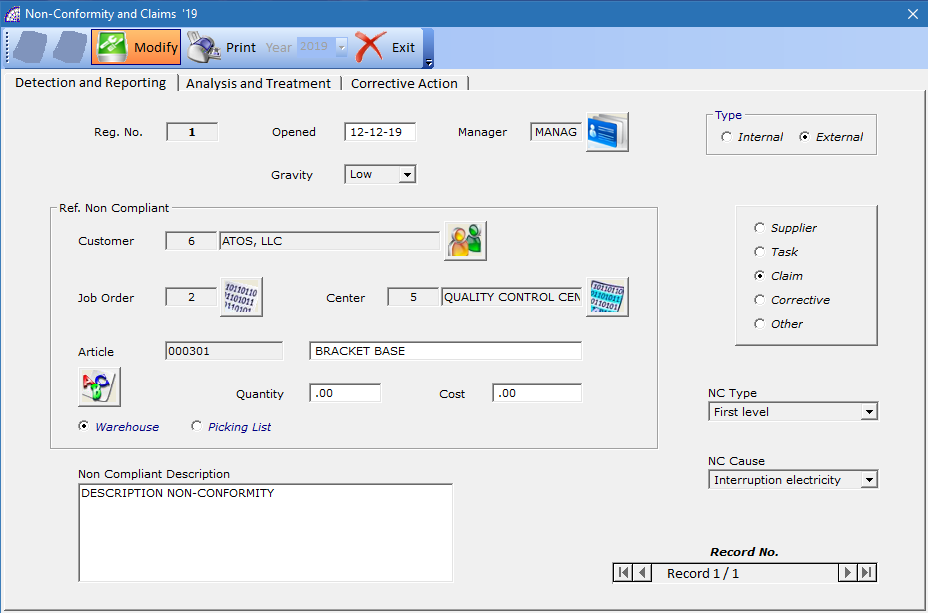
The management made available is basically divided into 2 distinct sections: Detection and Reporting, Analysis and Treatment.
In the first section, once the non-conformity has been opened, the various fields must be detailed, defining the problems, the causes, the references to the documents, any notes.
Reg. No.: displays the movement number, it is automatically created by the program.
Open the: opening date non-compliance.
Gravity: defines the severity level (Low, Average, High). It is a significant field, also present in the research conditions foreseen by the analysis phases (from the main menu select “Quality” + “NC Analysis …”).
Manager: a reference manager can be inserted, selected from the existing master data list (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Corporate Functions”).
Type: defines the type of conformity, internal or external.
Customer or Supplier: allows the insertion of the reference master data. If “Supplier” is active in the options (right side), you will have to enter the supplier that caused the problem.
Job Order: allows you to enter the job order reference, after selecting the year of competence. It is valid if non-compliance refers to this type of production document.
Center: select the reference work center (if required), from the existing master data list (from the main menu select “@/Arpro” + “Work Centers”).
Article: select the reference article (if required).
Warehouse/Picking List: activate the warehouse or the picking list, to select the article with the previous command.
Quantity: indicate the quantity of material or article (if required).
Cost: indicate the cost (if required).
Non-Compliant Description: free note field.
Supplier, Task, Claim, Corrective, Other option: defines the type of non-compliance or who produced it.
NC Type: (mandatory field) defines the type of non-compliance, chosen from the personal data list (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Non-Conformity Type”).
NC Cause: (mandatory field) defines the type of cause, chosen from the personal data list (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Non-Conformity Causes”).
In the second section we find all the data related to the analysis and treatment provided.
Normally after creating a non-compliance and entered the data in the fields on the “Detection and Reporting” section; only after defining the solution, proceed by entering the data of the second section “Analysis and Treatment”.
Closed on the: indicates the date of closure of the non-compliance.
Scheduled: date of presumed closure.
Result: indicates the result after closing (Positive or Negative).
Manager: a reference manager can be inserted, selected from the existing master data list (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Corporate Functions”).
Treatment Description: free note field, to describe briefly the operation.
Treatment NC: indicates the type of treatment of non-compliance (Accept prior Customer Authorization, Discard, Supplier Return, Re-Work, Other).
Time/Cost Resolution (h-m-s) – Cost per User: Time/Cost of resolution.
Raw Material Costs (if any): costs of raw material.
Dimensions: free field available to enter any dimensions.
Treatment Center: it is the treatment center (work center), selected from the master data list (from the main menu select “@/Arpro” + “Work Centers”).
Various Notes: free note field.
Toolbar
creates a new movement of non-compliance.
delete the current movement.
activates the edit of the current movement.
NON-CONFORMITY LIST …
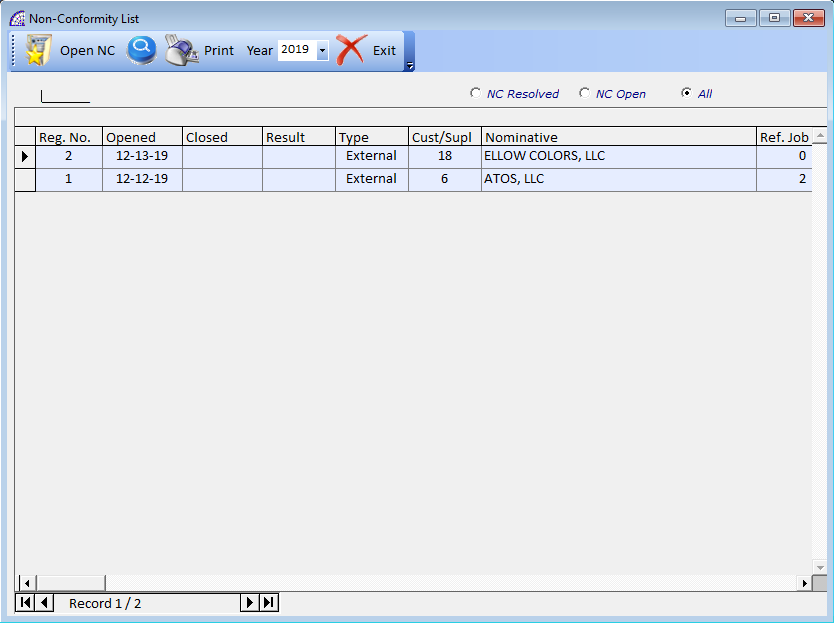
Displays a window listing with the non-compliance created. It is possible to apply filters to limit the display for: NC Resolved, NC Opened, All.
Open NC: opens the selected movement.
Year: allows the selection of the year of competence.
NC ANALYSIS …
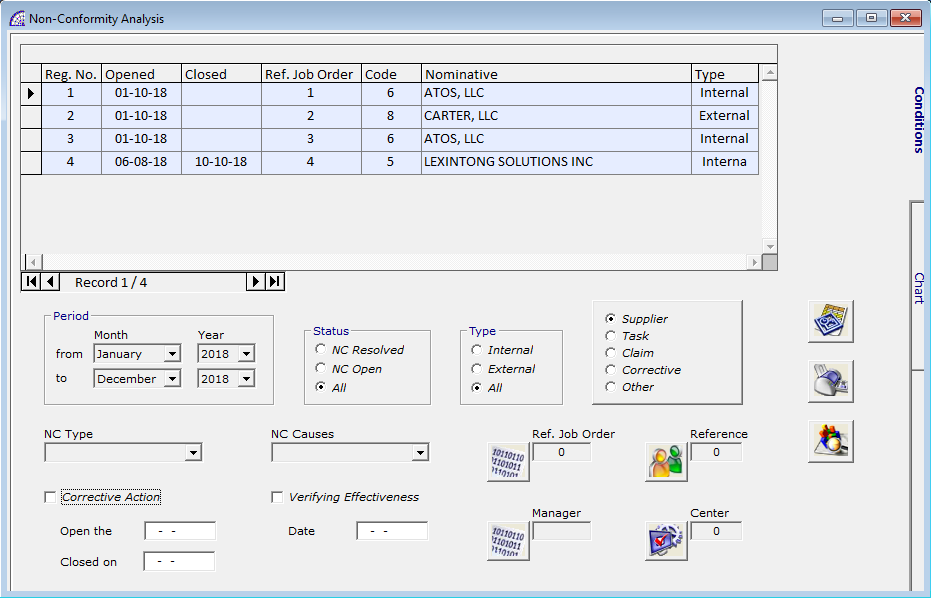
It is the tool for analysis and verification, which allows to understand and act where we have to improve in the business system.
The window is divided into 2 distinct sections: Conditions and Chart.
The first one is dedicated to the various search conditions in order to extract information from the introduced non-conformance movements, which respect the filter conditions set. We find conditions for period, status, type of non-compliance, chart type to obtain, NC Type, NC Causes, Ref. Job Order, Reference, Manager, Center.
In the grid above we find the list of non-compliance movements obtained after applying the search conditions, and pressed the calculation button.
The program calculates the displayed movements, opens the second section of the window and displays the corresponding graph.
In the grid above it are shown the work centers or the type of non-compliance found, depends on the choice made in the previous section (Chart Type); extracted from the movements and that allow to generate data for the graph.
The displayed graph can be represented in lines, bars or pies, in 2D or 3D, acting in the relative toolbar.
This tool can be used as many times as it may be necessary, without limitations, works in real time on the non-compliance movements introduced into the system.
CONTROL REPORTS
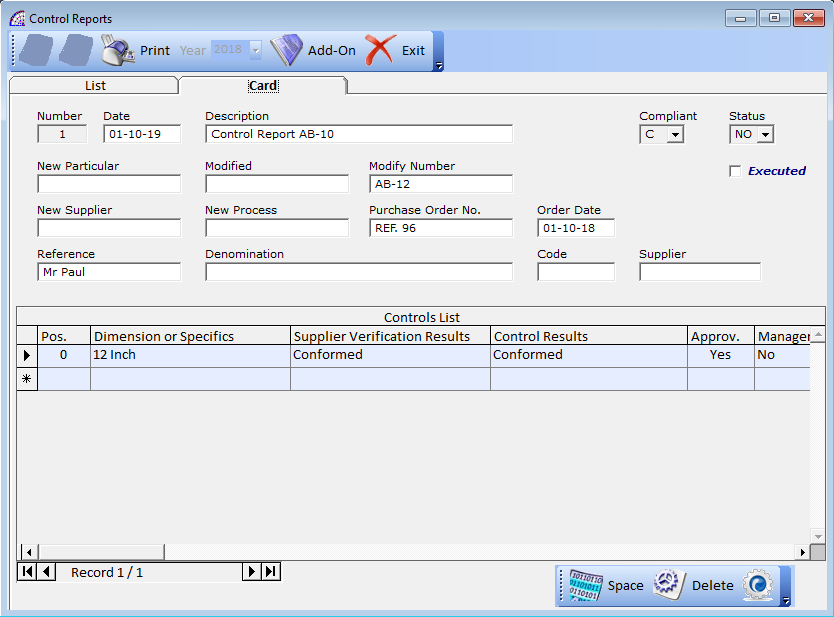
A feature dedicated to the introduction of analytical data regarding checks carried out in terms of quality, in relation to the company’s instruments and equipment or for other activities.
Similar to the management of non-compliance movements, these documents are managed year by year, so that those of previous years can also be consulted.
They must be created manually, taking care to insert the various head and body data of the individual document; in the body the column named “Pos.”, if the control interests the equipment, identifies the position of the same in the warehouse or in the various company departments.
A very important field that establishes the outcome of the test, documented by the individual movement, is given by the outcome: whether compliant or not.
All movements have a status that identifies if it has been terminated, canceled or suspended, as well as executed.
creates a new analysis movement.
cancel the selected movement.
print the list of displayed movements, in the selected year.
defines the reference year.
manages any external documentation (CRM), connected to the analysis and reporting system.
Card Tab
Number: displays the movement number. Automatically managed by the program, it is a progressive number.
Date: creation date.
Description: free description field to distinguish and to track the movement.
New Particular: alphanumeric field of 15 characters, will be used to identify the code of the new particular which replaces the old one.
Modified: alphanumeric field of 15 characters, the code of the modified particular may be indicated.
Modify Number: alphanumeric field of 15 characters, it can be used to indicate the modification number.
New Supplier: alphanumeric field of 15 characters, it can be used to indicate the new supplier involved in the verification.
New Process: alphanumeric field of 15 characters, it is possible to indicate a reference of the new verification process implemented.
Purchase Order No.: used to indicate the possible order number to supplier.
Order Date: indicates the date of the order.
Reference: reference of the operator who created the movement.
Denomination: alphanumeric field of 50 characters, reserved for an additional description of the movement.
Code: alphanumeric field of 10 characters, can be used for any additional code.
Supplier: alphanumeric field of 15 characters, can be used to identifies the supplier.
Compliant: serves to indicate if the movement is compliant (C) or non-compliant (NC).
Status: indicates the status of the movement (NO, YS, AN).
Executed: indicates if the movement was performed, then confirmed and terminated.
Control List Grid
In this section we find the list of the body lines of the movement or control report, entered and filled in manually by the operator. Each row has fields related to the single verification detail carried out on the instrument or equipment, by the reference supplier or certified company.
Pos.: it is a progressive number, managed by the program, to identify the position in the list of records present in the document.
Dimension or Specifics: alphanumeric field of 25 characters, defines physical characteristics of the instrument or controlled equipment.
Supplier Verification Results: alphanumeric field of 25 characters, reports the verification results from the supplier or certified company.
Control Results: alphanumeric field of 25 characters, reports a summary description of the control results.
Approv.: alphanumeric field of 5 characters, displays a code or an approval symbol of the check carried out.
Manager: a confirmation flag (Yes, No).
In the toolbar below we have the control of the body grid, considering that to insert new lines simply enter the data in the position corresponding to the last line.
adds a line of space above the selected record.
delete the current selected record.
it forces the recalculation of the “Pos.” field, on the inserted records, after having added intermediate records.
AUDITS
The purpose of an internal audit is to assess the effectiveness of your organization’s quality management system and your organization’s overall performance. Your internal audits demonstrate compliance with your planned arrangements.
Your organization will likely conduct internal audits for one or more of the following reasons:
- ensuring compliance to the requirements of internal, international and industry standards & regulations, and customer requirements;
- to determine the effectiveness of the implemented system in meeting specified objectives (quality, environmental, financial);
- to explore opportunities for improvement;
- to meet statutory and regulatory requirements;
- to provide feedback to the management
Each audit is a document that certifies the audit itself, containing all the elements of discussion and analysis. The @/Arpro Erp program, Quality Module, provides the document management system (CRM), with all its functions, perfectly integrated with the company production and accounting platform.
Once configured, it will be possible to connect (we are talking about links to the databases) various external documents, opening them directly in the system without having to leave the Quality platform. All the system will be organized in folders on the server computer, reserving privileges to open, modify and/or display to qualified personnel.
For each linked document inserted, it will also be possible to enter data in the various fields available (Notes, Ref. 1, Ref. 2, Date, Protocol), to facilitate researches and organization.
@Arpro Erp, Quality Module is sold without any reference document for the audits, even though we have different templates available that can be integrated if requested (under his own responsibility); just because considering the particular management it is necessary to turn to consultants in the field, specialized in the Quality system for companies.
Toolbar (CRM)
allows the creation of a new document, after selecting the type from the 3 proposed in the combobox list aside: “Document” for the Microsoft Word®, “Excel Sheet” for the Microsoft Excel®, “Drawing” for the Autodesk Autocad®.
The type of document created is copied from an existing template (Model.doc, Model.xls, Model.dwg), which can be customized with own company logos and formatting: the templates are all saved in the following server folder: \ArproW\Condivisa\Documents.
Selecting instead the document type “Image” in the combobox, the program disable this button in the toolbar and pressing the one with the open folder image aside, would be open a window to select an external file in bitmap format (Bmp).
Once the file has been selected, as in the previous case of creating a document from an existing model, the program inserts a link in the grid below with all the necessary data.
Each record of the grid has a reference to the type of document (Doc. Type), a network drive […], a complete path to the identification (Filename), an entry date (Date) and an automatically generated protocol number (Protocol). The remaining fields can be filled freely with data, even for identification: Notes (20 alphanumeric characters), Ref. 1 (numeric field), Ref. 2 (10 alphanumeric characters).
Last operative choice but not least, is given by the possibility to select without limits of format, external files; selecting the “Other …” mode, as for the previous modes, the program activates the button with the open folder image. This last choice is the most used to connect external files to the document management system (CRM), it represents the default.
deletes the reference of the selected document, excluding the real deletion of the external file which instead remains stored in the original folder.
The only condition that also allows the physical deletion of the external file, is if the latter was created by duplicating a model and it has been saved in the default folder mentioned above.
If active, pressing the cancel or print button in the toolbar, the program operates on all the records visible in the grid (not only in the one current selected).
send the selected document to the printer, without opening it. It works only for Microsoft Word® documents.
Models (available only in the @/Arpro CA, Agency Module): opens a management window dedicated to saving standard models, which can then be used in various contexts.
works only for Microsoft Word® documents, activates the auto-compilation of the selected document in the various “Bookmarks” inside it. The name of these “Bookmarks” must necessarily correspond to the name of the database fields, from which it automatically retrieves the data.
Imagining to organize the various documents in standard models, available to authorized users, and in these define “Bookmarks” in contexts of interest for self-compilation, such as for example names, personal data, etc., the program will simplify those phases often repetitive.
For more details, refer to the relative manual of the Microsoft Word® program, regarding the management of the “Bookmarks”, to specific advice to define the whole context, by contacting our sales departments.
Open: by double-clicking on the selected record or by pressing this button, the linked document will be opened. The system solves the problem of where the file is stored, if there are privileges from the operating system, and the file is opened by directly calling the creation program.
Any file format recognized by the Microsoft Window® platform is opened, if the CRM module is correctly configured.
is a search filter, where you can select the various typologies Add-On from the list, and consequently the program displays all the documents that have associated that type. Only during the insertion phase of a new document, if a type has been previously selected, the program associates it in the document as a search criterion.
Please consult the basic manual @/Arpro, regarding the specific management (from the program @/Arpro, in the main menu select “Master Data” + “Other” + “Typologies Add-On”).
In the specific management of the “Audits”, the program defines only one fixed filter item: “Verific”.
defines the network unit that will be used, if different from the default one, when creating/inserting a new document in the CRM.
In the grid, the network unit associated with the document is displayed in the “…” column.
opens a configuration file with a defined record layout, which configures the CRM system to be able to open the various linked documents, in the different formats provided and recognized by the Microsoft Windows® platform.
The configuration file is saved on the local computer, in the \ArproW\ Altro\Arpro-crm.ini folder, considering that every PC on the network can have different configurations.
It is mandatory to respect the syntax of the file, which provides for each inserted record, then the recognized file format, a string with the file extension, a separation string consisting of the characters “–”, a complete path to open the corresponding program.
For any changes made, press the button “Save” on the toolbar at the bottom of the configuration window.
CUSTOMER SATISFATION
Monitoring and measuring customer satisfaction is one of the important aspects of the quality system, as well as having to be the key element in general in doing business.
This approach would typically include defined responsibilities for logging and tracking complaints, clearing technical issues, determining problem causes and actions to address them. Specific examples of complaints must be sampled.
The link between the customer complaint process and corrective action also requires special scrutiny. Determine appropriate methods for monitoring and measuring customer satisfaction by:
- using customer satisfaction surveys;
- providing methods for receiving and dealing with customer feedback;
- providing suitable processes to monitoring trends in customer data.
There is no specific standard manual that can guide exactly in the processes to be followed, instead it is necessary, on the basis of its own activity, to find better quality standards to reduce the incidence of these problems.
It is therefore necessary to create a set of survey documents, suitable for your activity, where the business owner uses for the purpose of writing down the customer feedback assessments, in order to reveal customer expectations and improve customer retention.
They consist out of a set of questions related to motivation and buying experience. After collecting responses, the survey data is included into a report that highlights the company’s overall customer relationships.
@/Arpro Erp, Quality Module provides the platform to connect the various external documents, integrating data management with the production system and company accounting.
For the rest, the considerations made for the previous section regarding the management of the window Toolbar (CRM) are valid.
SUPPLIERS
All the quality procedures can help you and your suppliers create a systems approach to customer satisfaction.
The standard obligates a registered organization to create a QMS (Quality Management System) based on continual improvement rather than conformance to requirements, procedures and surveys.
Taking this into consideration, working with the suppliers to encourage them to think in terms of continual improvement. This will help them shift away from the traditional approach and move toward organizational development, monitoring and improvement.
It is therefore necessary to create a set of support documents, suitable for your activity, oriented to the control of the quality processes, quality and guaranteed provenance of the materials, performances, respect of average processing times.
Suppliers are therefore involved in the process of organization and efficiency of the entire system, aimed at customer satisfaction.
For the rest, the considerations made for the previous section regarding the management of the window Toolbar (CRM) are valid.
QUALITY MANUAL
The Quality Manual is the first level of documentation in a Quality Management System. Some organizations may combine the Quality Manual and Procedures into one manual, and refer to it as a quality manual.
The quality manual has multiple functions:
- It fully describes the scope of QMS;
- it completely explains each and every requirement of the ISO Standard;
- it contains complete detail and explanation of exclusions;
- it contains references for the quality procedures used to describe all the QMS processes;
- a flow chart represents the series and interaction of your key business processes;
- the organization’s quality policies which shows that the organization is strictly committed to quality
The primary use of the quality manual is as follows:
- to communicate management’s expectations for quality to the organization;
- to reveal the organization conformity with ISO requirements;
- to serve as a measure for compliance to management’s expectations for internal audits, ISO registrar audits, customer audits.
@/Arpro Erp, Quality Module provides the platform to connect the various external documents, integrating data management with the production system and company accounting.
For the rest, the considerations made for the previous section regarding the management of the window Toolbar (CRM) are valid.
INSTRUMENTS AND EQUIPMENT + MASTER DATA …
All monitoring and measurement equipment used for product and process verification must be controlled and calibrated against nationally traceable standards at specified intervals, as well as being cataloged and filed, inserting all the specific data.
The window dedicated to the instruments and equipment master data, and identification management allows the creation and insertion of the various data described.
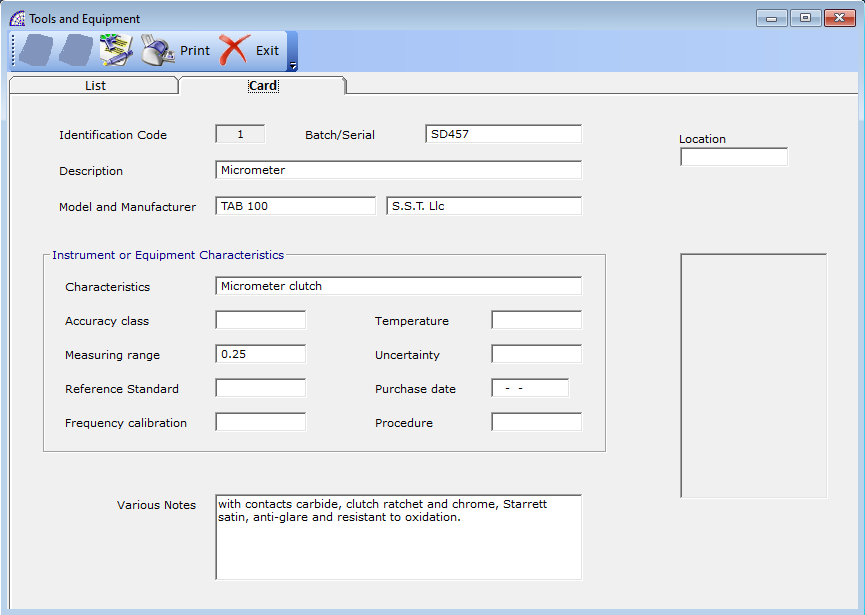
Once you have created a master data, you can enter data in the various fields available: Batch/Serial, Description, Model and Manufacturer, Location (in the company’s department), various characteristics and notes, an eventual picture of the instrument.
In this way every single instrument is cataloged, it will have its own identification code, it can be referred to within the normal scheduled maintenance activities.
Please take a look at the next two sections, “Instruments and Equipment + Maintenance and Calibrations” and “… + Maintenance Plans” and to the previous one “Control Reports”.
INSTRUMENTALS AND EQUIPMENT + MAINTENANCE AND CALIBRATIONS
Calibration ensures that your equipment performs within approved tolerances and delivers on safety and quality. Incorrect measurements compromise not only your reputation, but also safety and quality. The calibration of measuring and control equipment by an accredited supplier means that measurements are verified and traceable, thereby fulfilling quality system requirements as given, for example, in the ISO standards.
You should ensure that such devices are available to guarantee continuity of in-process measurement capabilities. All test equipment must be calibrated either:
- at regular, planned intervals
- or prior to use
Monitoring and measuring equipment must be:
- calibrated or verified at specified intervals or prior to use, based on recognized standards;
- adjusted or re-adjusted as necessary in accordance with manufacturer’s instructions;
- identified to enable calibration status to be determined;
- safeguarded from adjustment, which would invalidate measurement results;
- protected from damage or deterioration during handling, maintenance or storage
Each instrument should be traceable through its own calibration record which contains:
- identification number;
- manufacturer and model;
- frequency of calibration;
- reference standards used;
- Validation certificates and calibration findings;
- details of actions be taken in case of unsatisfactory results.
@/Arpro Erp, Quality Module provides the platform to connect the various documents about the maintenance and calibrations data, integrating data management with the production system and company accounting.
For the rest, the considerations made for the previous section regarding the management of the window Toolbar (CRM) are valid.
INSTRUMENTALS AND EQUIPMENT + MAINTENANCE PLANS
With an increasing concern of maintain the ISO Certification, it is necessary to provides a monthly maintenance plan for organizations to ensure compliance to the ISO Standard without the fear of being suspended.
The maintenance of the equipment is therefore particularly important, it must be managed to guarantee the quality standards imposed by the ISO procedures.
Thanks to this simple module, it is possible to record and maintain the entire equipment inventory of a company. After you plan, identify, communicate and assign maintenance, calibration and control tasks, with work orders and assignments.
It also allows you to quickly identify the location and status of equipment, maintain historical information and traceability and produce statistical information necessary for the analyses of Repeatability and Reproducibility.
@/Arpro Erp, Quality Module provides the platform to connect the various documents about the maintenance plans data, integrating data management with the production system and company accounting.
For the rest, the considerations made for the previous section regarding the management of the window Toolbar (CRM) are valid.
CORPORATE FUNCTIONS
It manages the master data of company functions, to be managed in the context of non-compliance (from the main menu select “Quality” + “Non-Conformity and Claims”).
For each it is necessary to insert a description, an acronym and eventually a note.
NON-CONFORMITY TYPE
It manages the master data of non-conformity type, used in the context of non-compliance movements.
For each it is necessary to insert a description and eventually a note.
NON-CONFORMITY CAUSES
It manages the master data of non-conformity cause, used in the context of non-compliance movements.
For each it is necessary to insert a description and eventually a note.
